Buy Cheap All-Natural Chicago CoQ10 Anti-Aging Herbal Supplements Vitamins
 Why pick our Natural CoQ10 Herbal Supplement?
Why pick our Natural CoQ10 Herbal Supplement?
There are many options available today when choosing vitamins and anti-aging supplements. This means that you have to be careful as a consumer and make sure you choose a reliable manufacturer who only uses the highest quality ingredients. The Chicago Center For Anti-Aging has partnered with one of the most reputable manufacturers which helps ensure the quality of our private line of vitamins and anti-aging supplements. Quality is what should be the most important attribute you should look for to help make your decision, not cost. Look for quality you can trust.
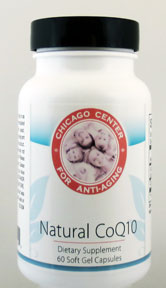
 Natural CoQ10
Natural CoQ10
Dose Form
 As a dietary supplement, 1 or more soft gel capsules per day or as recommended by your health care professional.
As a dietary supplement, 1 or more soft gel capsules per day or as recommended by your health care professional.
Other Ingredients
Rice Bran Oil, Gelatin, Glycerin, Purified Water, Yellow Beeswax, Carob Extract
and Caramel Liquid.
Rationale
CoQ-10 (Ubiquinone), one of many biological molecules in the quinone family, is a vital component to electron-generated energy
in all cells.
Tissues with high levels of CoQ10 (mcg/gram tissue)
- Heart 114.0
- Kidney 66.5
- Liver 54.9
- Muscle 39.7
- Pancreas 32.7
- Brain 13.4
- Colon 10.7
Research Findings
- CoQ-10 is capable of reducing lipid peroxidation directly or indirectly by maintaining the vitamin E pool1. This is particularly important in lowering LDL oxidation. Coenzyme Q-10 is a fat-soluble molecule, ideally suited for this task.More international trials have been conducted on coenzyme Q than on any cardiovascular drug for heart failure, with the results favoring the use of CoQ10 in the prevention and treatment of this condition.
- Meta-analysis2 — 14 Studies published between 1984-94 showing a consistent increase in both stroke volume and cardiac output (76% and 73% over placebo, respectively). Consistent improvements were also seen in cardiac index, ejection fraction and end diastolic volume index.
- Large Multi-center study3 — 2664 patients from 173 centers with heart failure (NYHA II and III) were given 50-150 mg of
- CoQ10 daily and assessed 90 days after beginning treatment (78% were given 100 mg/day). Side-effects were low (1.5%).
- Clinical signs and symptoms were reduced by at least 50% in all categories, and greater than 70% in most of the 12 categories tested (8 of 12).
- Long-term, multi-center study4 — 641 patients with NYHA class III and IV congestive heart failure receiving conventional treatment were given placebo (n=322) or CoQ-10 (n=319) at 2 mg/kg per day for 1 year (equal to 136 mg for a 150 lb individual). Hospitalizations for worsening heart failure was statistically lower in the CoQ-10 group, as were episodes of pulmonary edema and cardiac asthma.
- Long Term Study5 — 424 patients (1985-93) with various cardiovascular diseases were treated with Coenzyme Q10 (75-600 mg/day- average 242 mg). Patients were divided into 6 categories: ischemic cardiomyopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy,primary diastolic dysfunction, hypertension, mitral valve prolapse and valvular heart disease. Patients were followed, on
average, for 18 months. Of the 424 patients 58% improved by one NYHA class, 28% by 2 classes and 1.2 by three classes.
- Heart medication was reduced in patients taking CoQ10. 43% stopped taking between 1 and 3 drugs and only 6% required the addition of one drug.
- Double-blinded, placebo controlled trial6 — 47 patients with coronary artery disease (acute myocardial infarction, angina pectoris or unstable angina) with raised lipoprotein(a) levels were assigned coQ10 (60 mg bid) or placebo. Serum lipoprotein(a) was significantly reduced in the coQ10 group. HDL cholesterol was increased significantly, improving the HDL/LDL profile.
- Studies during the 1990’s have shown that supplemental CoQ-10 is capable of lowering blood pressure in small clinical trials.
- Double-blind Clinical Trial7 —59 hypertensive patients receiving hypertensive medication were given oral coenzyme Q10 (60 mg bid) or B-vitamin complex. After 8 weeks, there was a decrease in both the systolic pressure (168 mmHg to 152 mmHg) and the diastolic pressure (106 mmHg to 97 mmHg) in the CoQ-10 group, while there was essentially no change in the B-vitamin group.
- As with many antioxidants, diabetics have reduced levels of coenzyme Q10. There are several studies which suggest that coQ-10 supplementation reduced fasting blood sugar, and another showed reduced ketone bodies. While more studies need to be done, CoQ-10 seems safe for diabetic patients and may be of some benefit.
- The use of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statin drugs) for the reduction of serum cholesterol is common. It is well established that these drugs lower serum CoQ-10 levels8.
- While there have been reports that patients with periodontal disease have a decreased level of CoQ-10 in gingival tissues10, few good studies have been done to determine if CoQ-10 has a place in treating periodontal disease.
- Lead by Folkers research on mammary tumors in animals, CoQ10 supplements were added to therapy in cases of breast tumors. In 1993, this led to complete regression of tumors in two cases of breast cancer11. Similar reports have followed these studies. The dose used for these cases was 390 mg per day. More recently, a coenzyme Q10 deficiency was noted in patients with both carcinomas and non-malignant lesions of the breast12.
- Clinical Trial9 — 34 hypercholesterolemic patients were given either 20 mg of simvastatin or 20 mg of simvastatin and 100mg CoQ-10 per day. Both groups had a significant drop in serum cholesterol but the group without supplemental CoQ-10 had significantly lower serum and platelet CoQ-10 levels. The group receiving 100mg per day of CoQ-10 increased CoQ-10 levels significantly in both serum and platelets.
Dose
As a dietary supplement, 1 or more soft gel capsules per day or as recommended by your health care professional.
Contraindications, Adverse or Other Reactions
If you are pregnant or nursing, consult your physician before taking this product. This product contains the following potential allergens: soy. Those taking blood thinning medications should use caution.
How can I purchase this Natural CoQ10 Vitamin?
Even if you are not a member of the Chicago Center For Anti-Aging, you can still purchase any of our private and unique anti-aging supplements and vitamins. You can drop by our office anytime and pick up any of our products. We are conveniently open 7 days a week from 8am-8pm.
If you want to place an order for delivery, call us at 847.696.9900 and you can order anything you want. Mention our website and you will receive 2 day USPS shipping for any sized order for only $5!
Finally, you can also order online at www.buycheapbargains.com, which is the only place online allowed to sell our products...
References
1. Thomas SR, Neuzil J, Stocker R. Cosupplementation with coenzyme Q prevents the prooxidant effect of alpha-tocopherol and increases the resistance of LDL to transition metal-dependent
oxidation initiation. Arterioscler Throm Vasc Biol 1996; 16(5):687-696
2. Soja AM, Mortensen SA. Treatment of congestive heart failure with coenzyme Q10 illuminated by meta-analysis of clinical trials. Mol Aspects Med 1997; 18 Suppl::S159-S168
3. Baggio E, et al. Italian multicenter study on the safety and efficacy of coenzyme Q10 as adjunctive therapy in heart failure. CoQ10 Drug Surveillance Investigators. Mol Aspects Med 1994;
15 Suppl: S287-S294
4. Morisco C, Trimarco B, Condorelli M. Effect of coenzyme Q10 therapy in patients with congestive heart failure: a long-term multicenter randomized study. Clin Investig 1993; 71(8Suppl):
S134-6
5. Langsjoen H, Folkers K, et al. Usefulness of coenzyme Q10 in clinical cardiology: a long-term study. Mol Aspects Med 1994; 15 Suppl: S165-S175
6. Singh RB, Niaz MA. Serum concentration of lipoprotein(a) decreases on treatment with hydosoluble coenzyme q10 in patients with coronary artery disease: discovery of a new role. Int J
Cardiol 1999; 68(1):23-9
7. Singh RB et al. Effect of hydrosoluble coenzyme Q10 on blood pressure and insulin resitance in hypertensive patients with coronary artery disease. J Hum Hypertens 1999; 13(3):203-8
8. Mortensen SA et al. Dose-related decrease of serum coenzyme Q10 during treatment with HMG-C0A reductase inhibitors. Mol Aspects Med 1997; 18 Suppl: S137-44
9. Bargossi AM et al. Exogenous CoQ10 supplementation prevents plasma ubiquinone reduction induced by HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Mol Aspects Med 1994; 15 Suppl:S187-93
10. Hansen IL et al. Bioenergetics in clinical medicine. IX. Gingival and leucocytic deficiencies of coenzyme Q10 in patients with periodontal disease. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol
1976; 14(4):729-38
11. Lockwood K, Moesgaard S, Folkers K. Partial and complete regression of breast cancer in patients in relation to dosage of coenzyme Q10. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1994;
199(3):1504-8
12. Jolliet P et al. Plasma coenzyme Q10 concentrations in breast cancer: prognosis and therapeutic consequences. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 1998; 36(9):506-9
** Information for health care professionals only.
** These statements have not been evaluated by the FDA. This product is not intended to treat, diagnose, prevent, or cure any disease. Consult a physician before taking. Should you experience any serious physical side effects from taking these nutritional supplements, discontinue and call your doctor immediately.